Call or Text us at
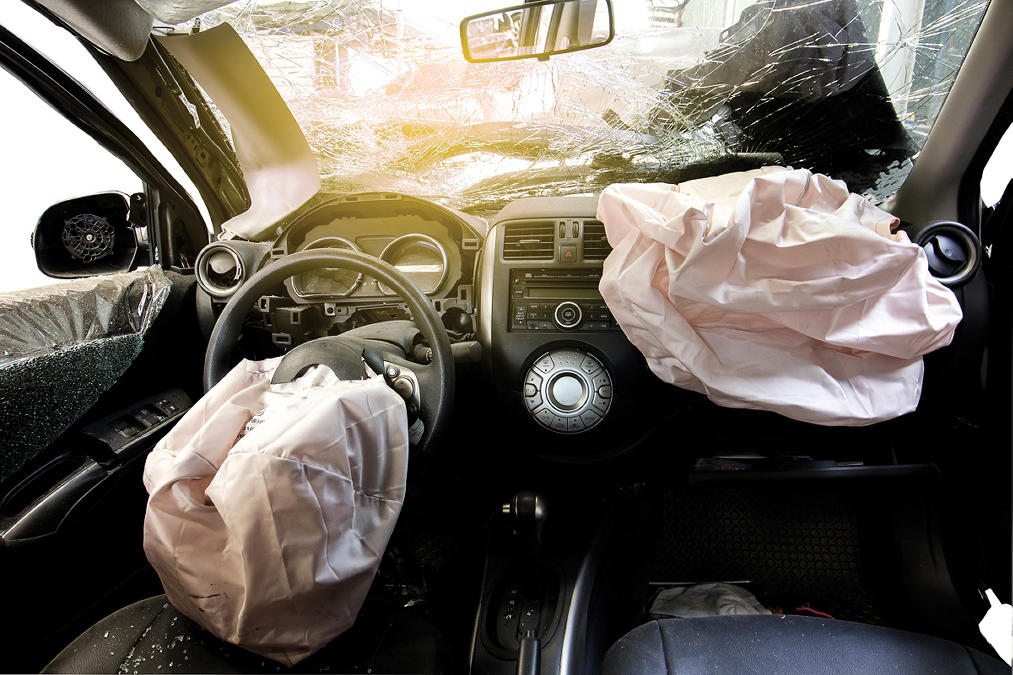


At Beach Auto Repair, our proficient technicians specialize in addressing
issues concerning car airbag systems. Whether it's a lit airbag warning light, a
deployed airbag, or a malfunctioning sensor, our team swiftly diagnoses the problem
and proceeds with the necessary repairs.
A lit airbag warning light, a deployed airbag due to a collision, or a faulty sensor
can be attributed to a variety of issues within the airbag system. Our experts are
skilled at efficiently and effectively resolving these problems, ensuring your
vehicle's safety features are fully functional. Don't hesitate to reach out to us
for top-quality airbag system services that guarantee a secure and well-protected
driving experience.
Call or Text us at
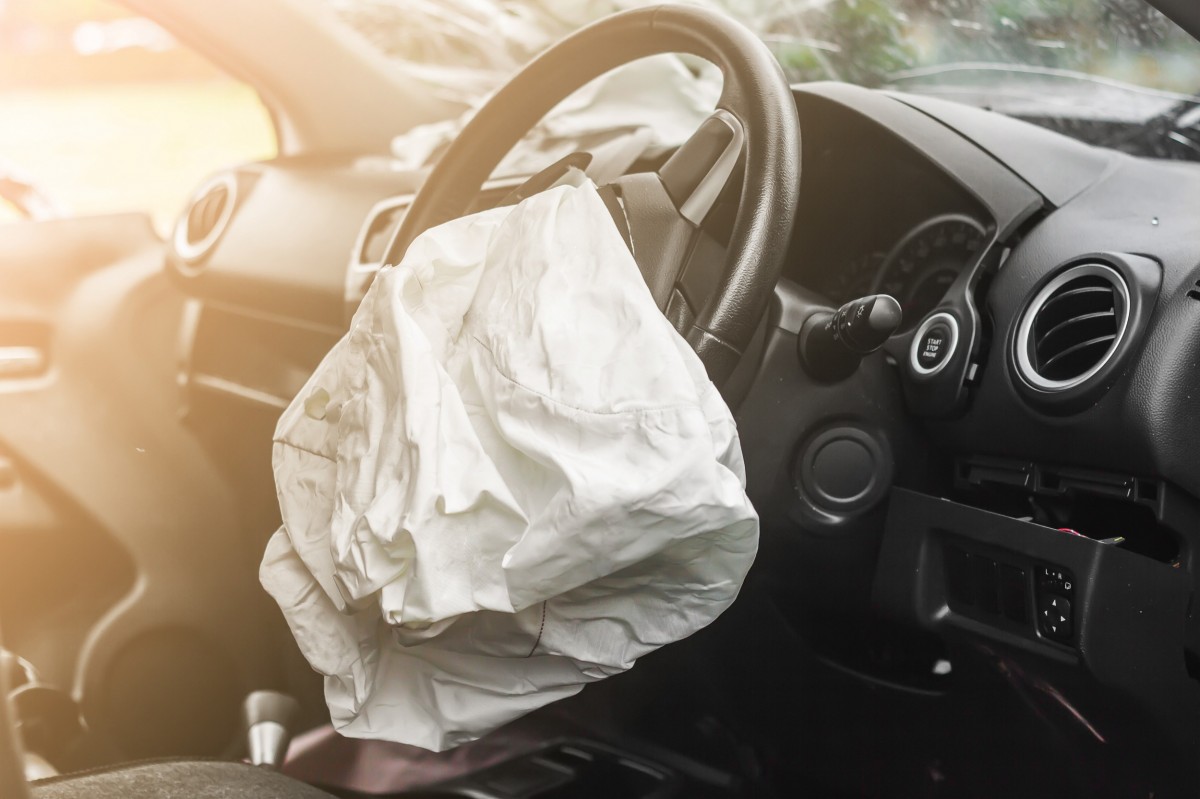
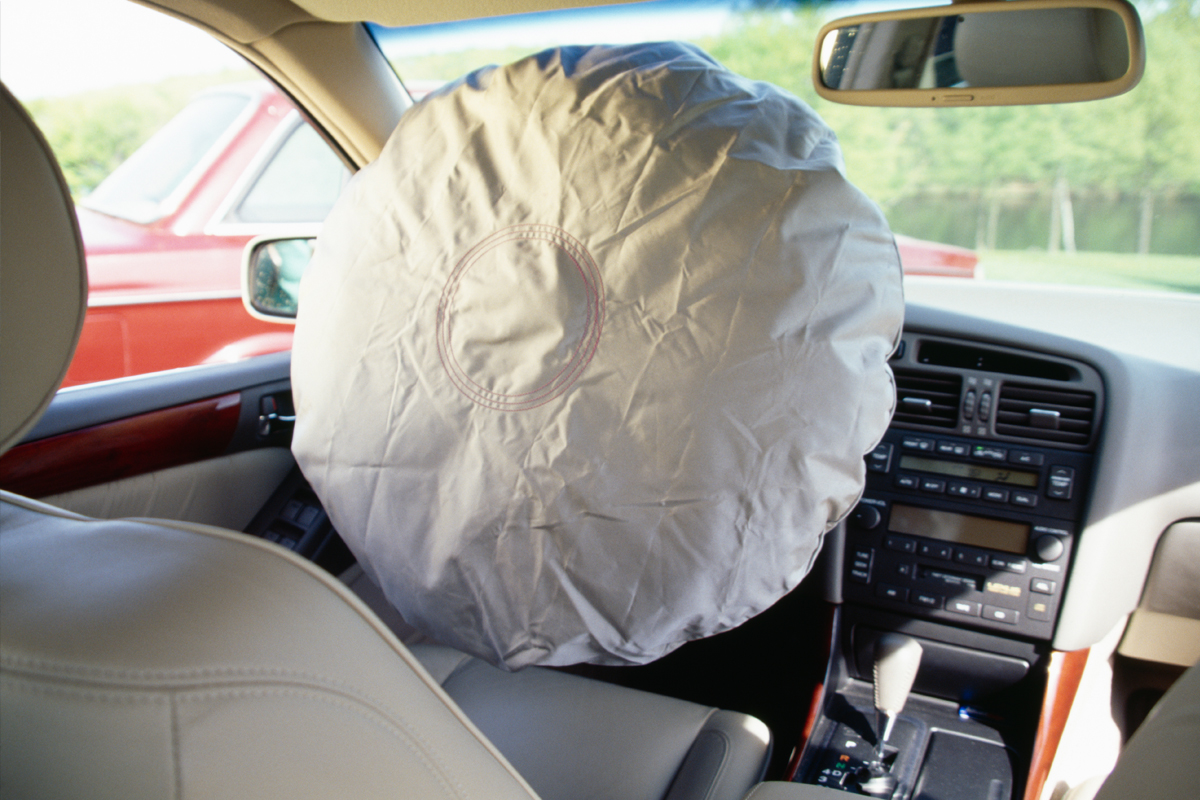
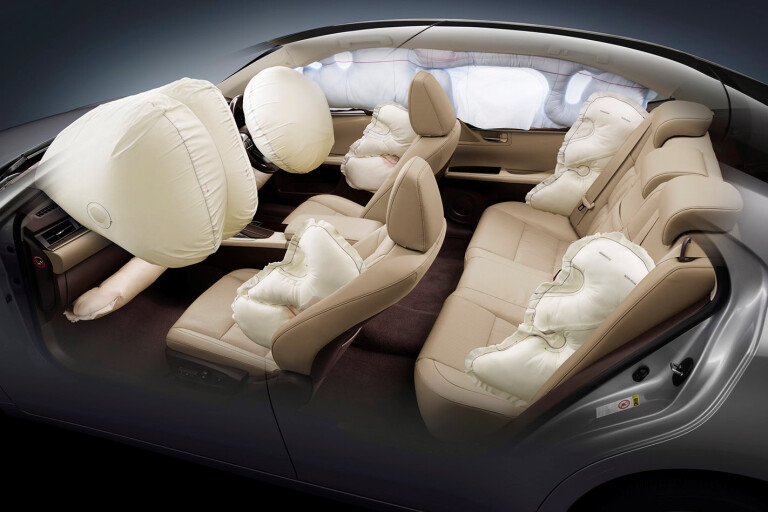





Understanding the purpose of automotive airbag systems is crucial for comprehending their role in enhancing occupant safety. Here are some key points to consider:
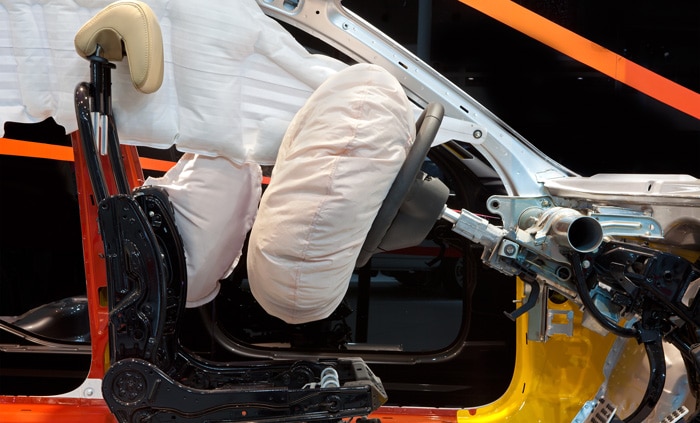
1. Occupant Protection: The primary purpose of automotive airbag systems is to provide an additional layer of protection for vehicle occupants during collisions and accidents.
2. Collision Energy Absorption: Airbag systems work in conjunction with seat belts to absorb and distribute the energy generated during a collision. This reduces the force exerted on occupants and minimizes injury risks.
3. Deceleration Assistance: Airbags help slow down the rate of deceleration experienced by occupants during a collision, reducing the chances of severe injuries caused by sudden stops.
4. Head and Chest Protection: Depending on the location of airbags, they can offer protection to the head, chest, and upper body areas, safeguarding against impact with the vehicle's interior or hard surfaces.
5. Side Impact Safety: Side airbags provide protection in side-impact collisions by deploying between the door and the occupant, reducing the likelihood of head or torso injuries.
6. Rollover Protection: Some advanced airbag systems include rollover sensors that trigger airbag deployment to protect occupants during vehicle rollovers.
7. Collision Severity Adaptation: Airbag systems are designed to deploy with varying force based on the severity of the collision. This ensures optimal protection without unnecessary deployment in minor incidents.
8. Supplemental Restraint: Airbag systems work in tandem with seat belts as part of a vehicle's comprehensive restraint system, enhancing the overall effectiveness of occupant protection.
9. Reducing Secondary Impact: In high-speed collisions, airbags prevent occupants from striking hard interior components like the steering wheel, dashboard, or windshield, reducing secondary injuries.
10. Enhancing Safety for All Ages: Airbag systems consider various factors such as seat occupancy, seatbelt usage, and collision force to adjust airbag deployment, enhancing safety for occupants of different sizes and ages.
11. Frontal and Rear Collisions: Frontal airbags deploy in frontal collisions, while advanced systems include rear-seat airbags to protect rear passengers during rear-end collisions.
12. Advanced Safety Features: Airbag systems are integrated with vehicle safety technologies such as crash sensors, electronic control units, and deployment algorithms for precise and timely deployment.
13. Emergency Responder Assistance: Deployed airbags can also help emergency responders assess collision severity and determine the appropriate course of action.
14. Reduction of Fatalities and Injuries: The overall purpose of airbag systems is to reduce the risk of fatal injuries and minimize the severity of injuries sustained by vehicle occupants during accidents.
By understanding these multifaceted purposes of automotive airbag systems, you gain insight into their critical role in enhancing vehicle safety for both drivers and passengers.
Understanding common failures of automotive airbag systems is vital for ensuring occupant safety. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Faulty Airbag Sensors: Airbag deployment relies on sensors that detect impacts and collisions. If these sensors malfunction or fail to detect a crash, the airbags might not deploy when needed.
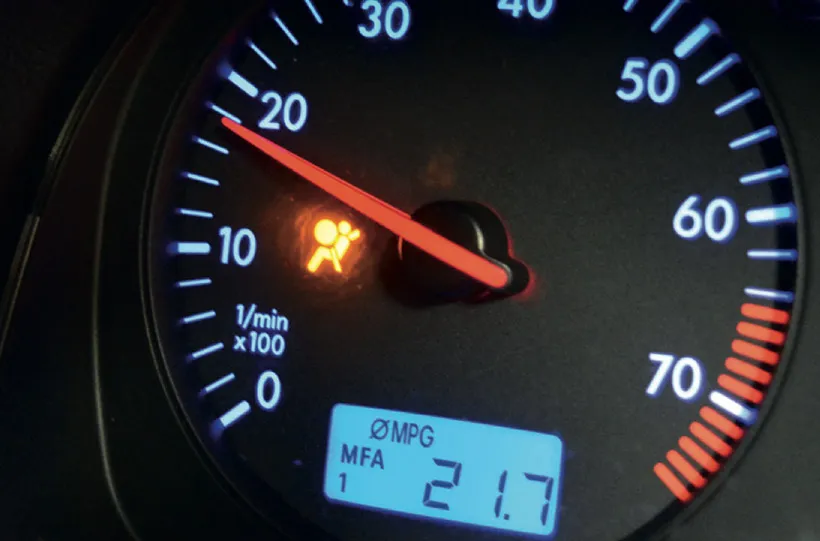
2. Airbag Warning Light: The airbag warning light on the dashboard indicates a problem in the airbag system. Ignoring this light can lead to non-deployment or unintended deployment.
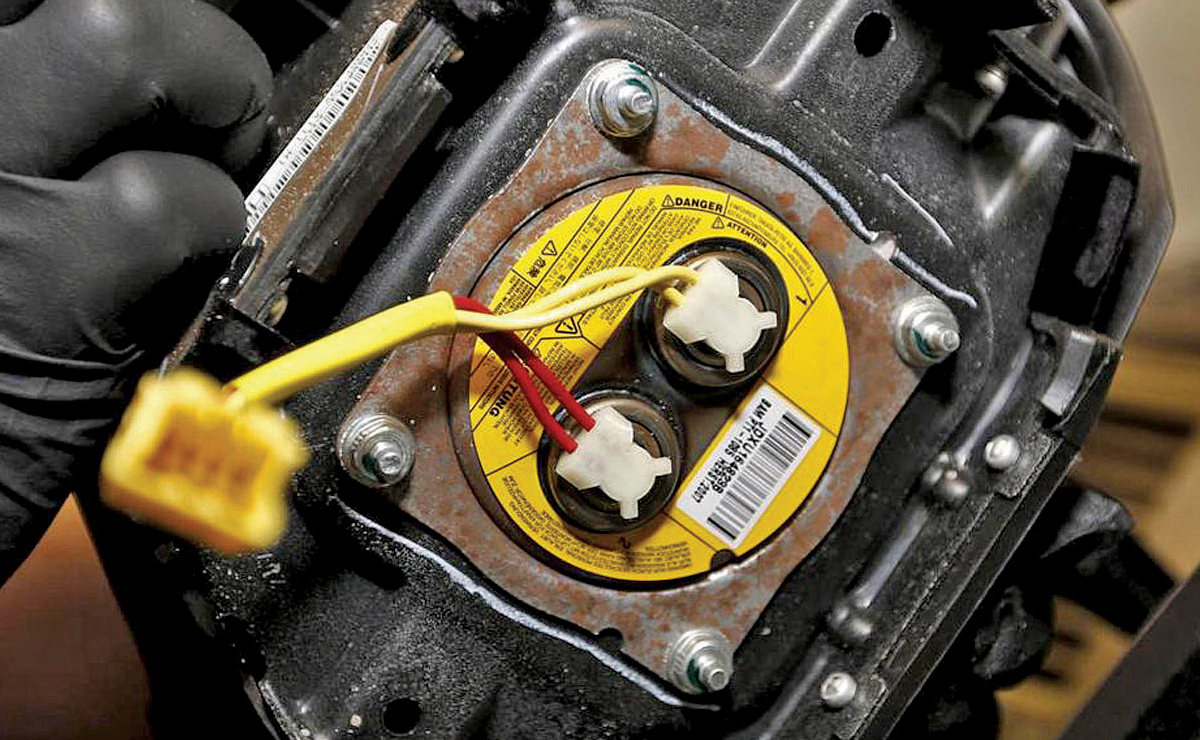
3. Clock Spring Failure: The clock spring is an electrical connection that allows the steering wheel to turn while maintaining a connection to the airbag and other controls. A failed clock spring can prevent airbag deployment during a collision.
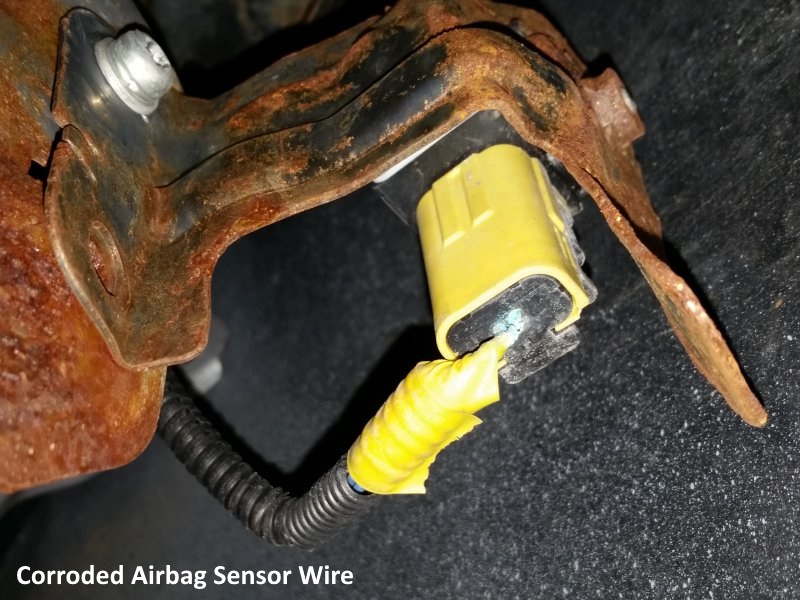
4. Electrical Issues: Wiring problems, loose connections, or damaged connectors within the airbag circuit can prevent proper deployment or lead to unintended airbag activation.
5. Seat Belt Pretensioner Malfunction: Seat belt pretensioners tighten the seat belts during a collision to restrain occupants. Malfunctioning pretensioners may not secure occupants properly.
6. Inflator Defects: Inflators are responsible for deploying the airbag. Defective inflators can rupture during deployment, causing metal fragments to be expelled, posing a serious safety risk.
7. Unintended Airbag Deployment: In rare cases, airbags might deploy unexpectedly, potentially causing injuries to vehicle occupants.
8. Impact Sensor Issues: Impact sensors detect crash severity and trigger airbag deployment. Malfunctioning sensors can lead to delayed or improper airbag deployment.
9. Tampering or Disconnection: Attempting to disable or tamper with the airbag system can render it ineffective or cause unintended deployment.
10. Sensor Interference: Installing aftermarket equipment near airbag sensors or routing wires through these areas can interfere with sensor operation.
11. Excessive Corrosion: Corrosion or water damage can affect sensor operation, wiring, and connectors, leading to system failure.
12. Age and Wear: Over time, components within the airbag system can deteriorate, leading to reduced effectiveness or malfunction.
13. Recalls and Defects: Stay informed about recalls related to your vehicle's airbag system. Manufacturers issue recalls to address potential safety concerns.
14. Impact to Body Structure: Severe collisions that damage the vehicle's body structure can affect the airbag deployment path and timing.
15. Non-Deployment Zones: Some airbags might not deploy in certain areas of the vehicle, such as behind the driver in a rear-end collision.
By understanding these common airbag system failures, you can take preventive measures, address issues promptly, and ensure the safety systems in your vehicle are functioning as intended.
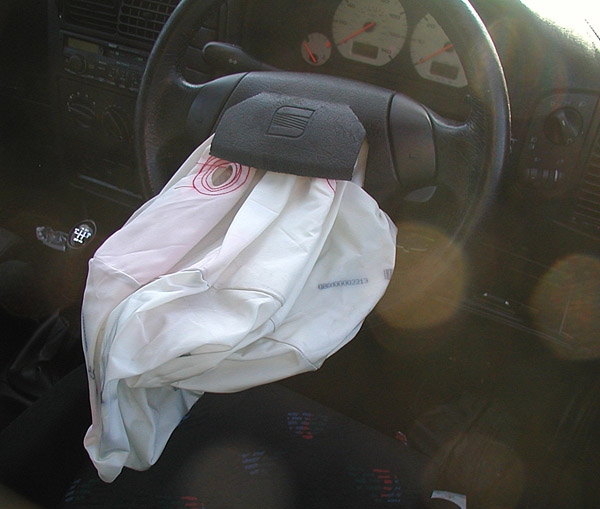
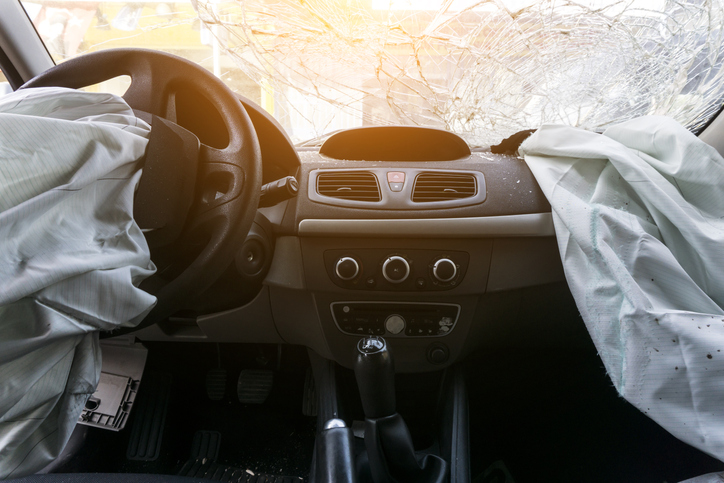



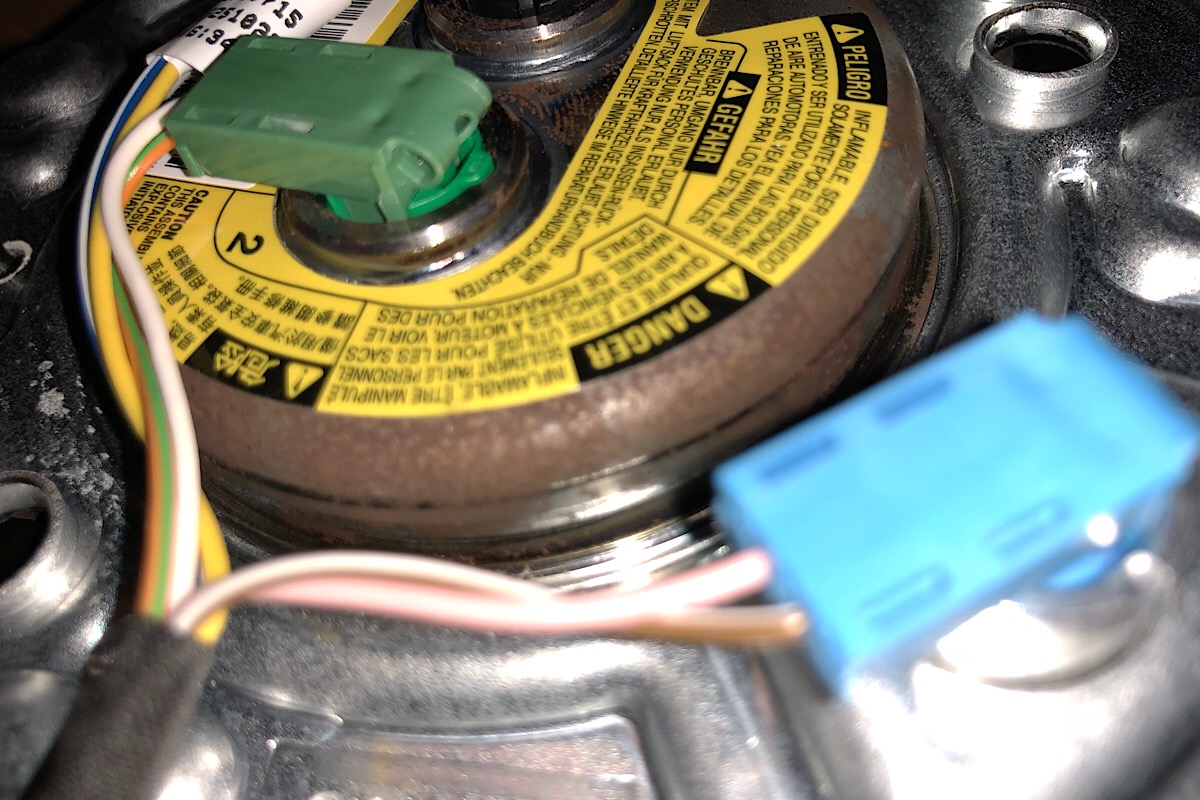






Properly servicing automotive airbag systems is crucial for ensuring the safety of vehicle occupants. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Professional Inspection: Airbag systems are complex and sensitive safety components. If you suspect an issue or if the airbag warning light is illuminated, seek a professional mechanic with experience in airbag system diagnostics.
2. Airbag Warning Light: If the airbag warning light on the dashboard is illuminated, it indicates a problem in the airbag system. Address the issue promptly to ensure the system's functionality.
3. Regular Maintenance: Include airbag system inspection as part of your regular vehicle maintenance routine, especially after collisions or accidents, to ensure the system is intact and functional.
4. Battery Disconnection: When performing maintenance that involves disconnecting the battery, follow manufacturer guidelines to prevent unintentional airbag deployment due to electrical disruptions.
5. Clock Spring Replacement: If you experience problems with horn function, steering wheel controls, or the airbag warning light, a malfunctioning clock spring may be the cause. Have it replaced by a professional.
6. Seat Belt Pretensioner Inspection: Seat belt pretensioners play a critical role in occupant restraint. If you notice irregularities or the airbag warning light is on, have the system inspected.
7. Sensor Calibration: After certain repairs or replacement of airbag system components, sensor recalibration might be necessary to ensure accurate deployment in case of a collision.
8. SRS Diagnostic Scan: Periodically conduct a diagnostic scan of the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) to identify potential issues and ensure proper functionality.
9. Recall Checks: Stay informed about recalls related to your vehicle's airbag system. Manufacturers issue recalls to address potential safety concerns.
10. Genuine Parts: Use genuine OEM parts when replacing airbag system components to ensure compatibility and adherence to safety standards.
11. Avoid DIY Repairs: Airbag systems are intricate and sensitive. Avoid attempting DIY repairs on airbag components, as improper handling can result in unintended deployment or system malfunction.
12. Protection During Repairs: If you need to perform repairs near airbag components, follow safety guidelines and precautions to prevent accidental deployment.
13. Documentation: Keep records of airbag system maintenance and repairs. This documentation can be valuable for maintaining the vehicle's history and addressing potential future issues.
14. Training and Certification: Seek out mechanics who are certified to work on airbag systems. Proper training ensures the correct diagnosis and resolution of airbag-related problems.
15. Post-Collision Inspection: After a collision, have a qualified professional inspect the airbag system, even if the airbags didn't deploy. Some systems may still be affected and need attention.
By understanding these key points and staying proactive in servicing your automotive airbag system, you can ensure the safety features are operating as intended, contributing to the overall safety of your vehicle.
Let us know how we can help.