Call or Text us at
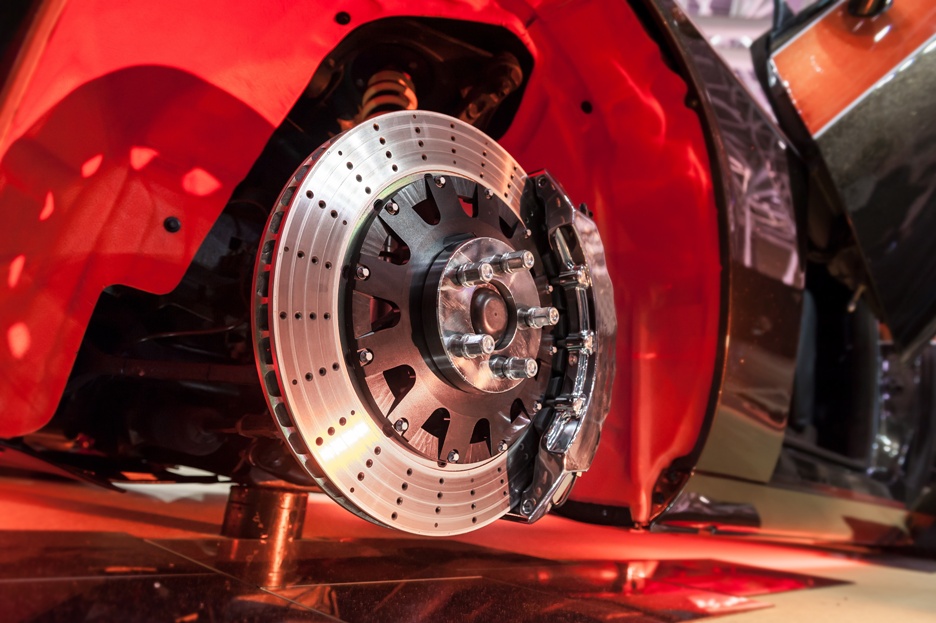


At Beach Auto Repair, our experienced technicians specialize in addressing issues
related to car brakes and rotors. Whether it's squeaking brakes, a pulsating brake
pedal, or worn-out rotors, our team swiftly diagnoses the problem and proceeds with
the necessary repairs.
Squeaking brakes, a pulsating brake pedal, or unevenly worn rotors can be attributed
to worn brake pads or damaged rotors. Our experts excel at efficiently and
effectively resolving these problems, ensuring your vehicle stops safely and
smoothly. Feel free to contact us for top-tier brake and rotor services that
guarantee a secure and reliable driving experience.
Call or Text us at
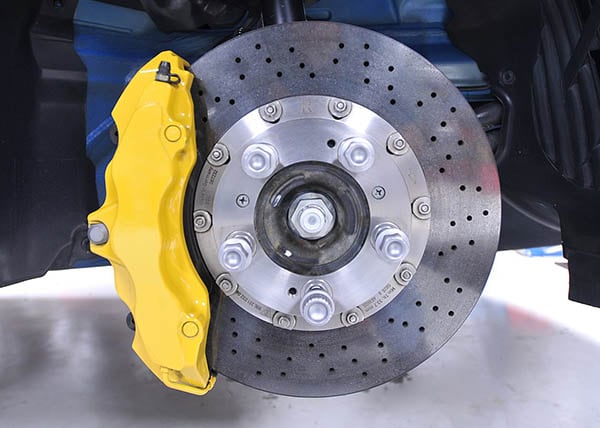
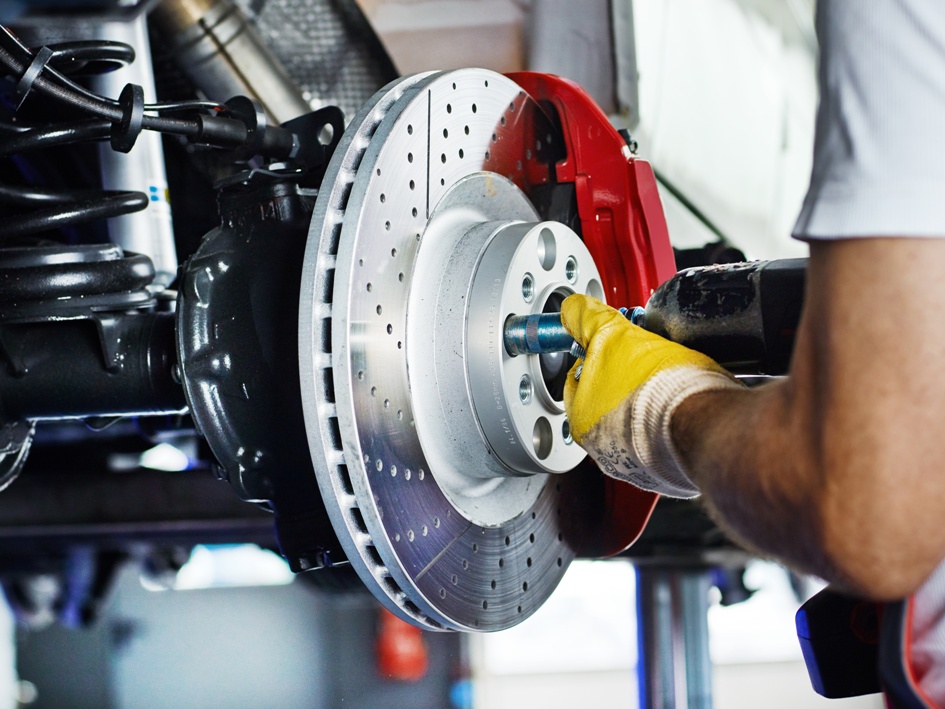
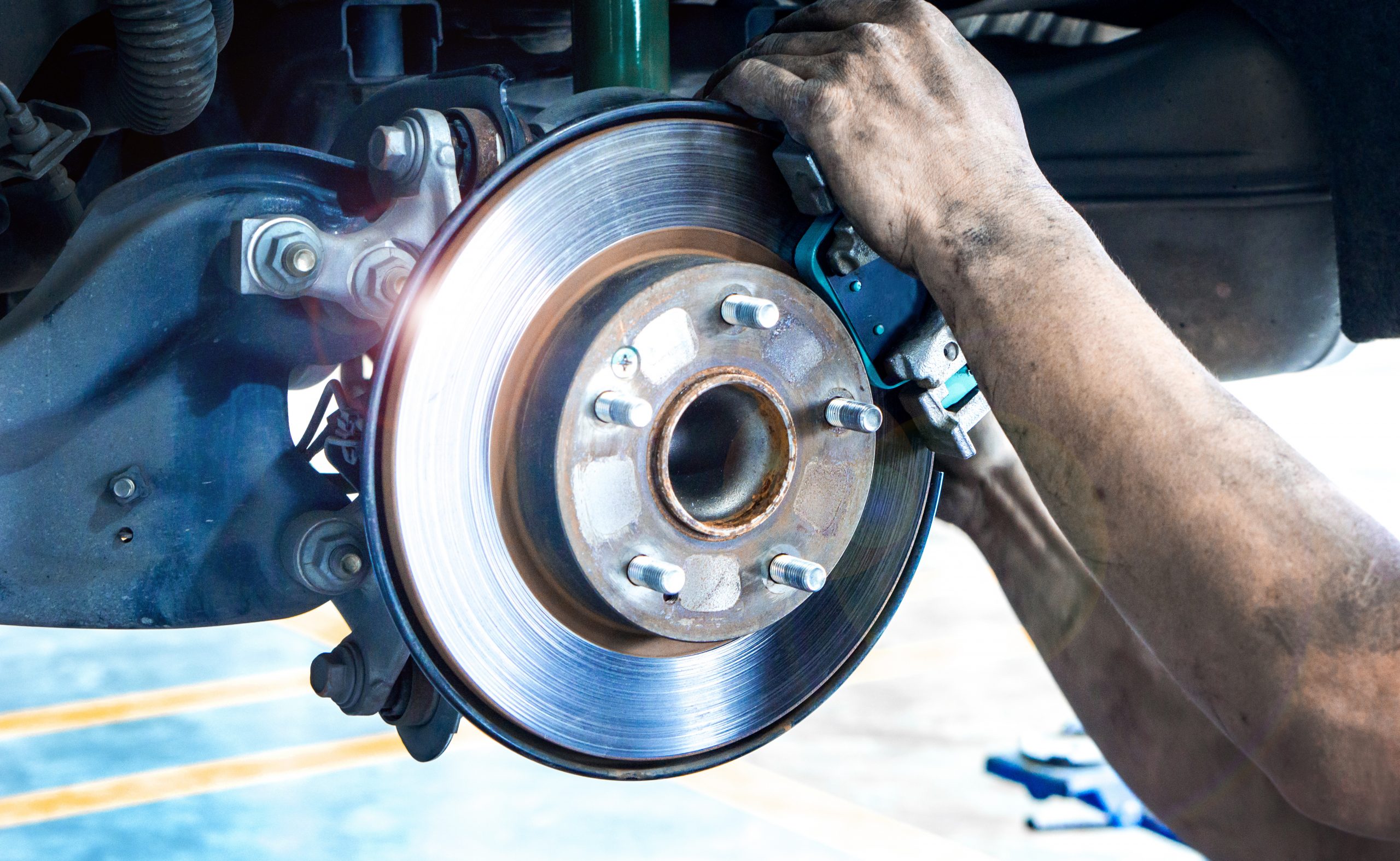



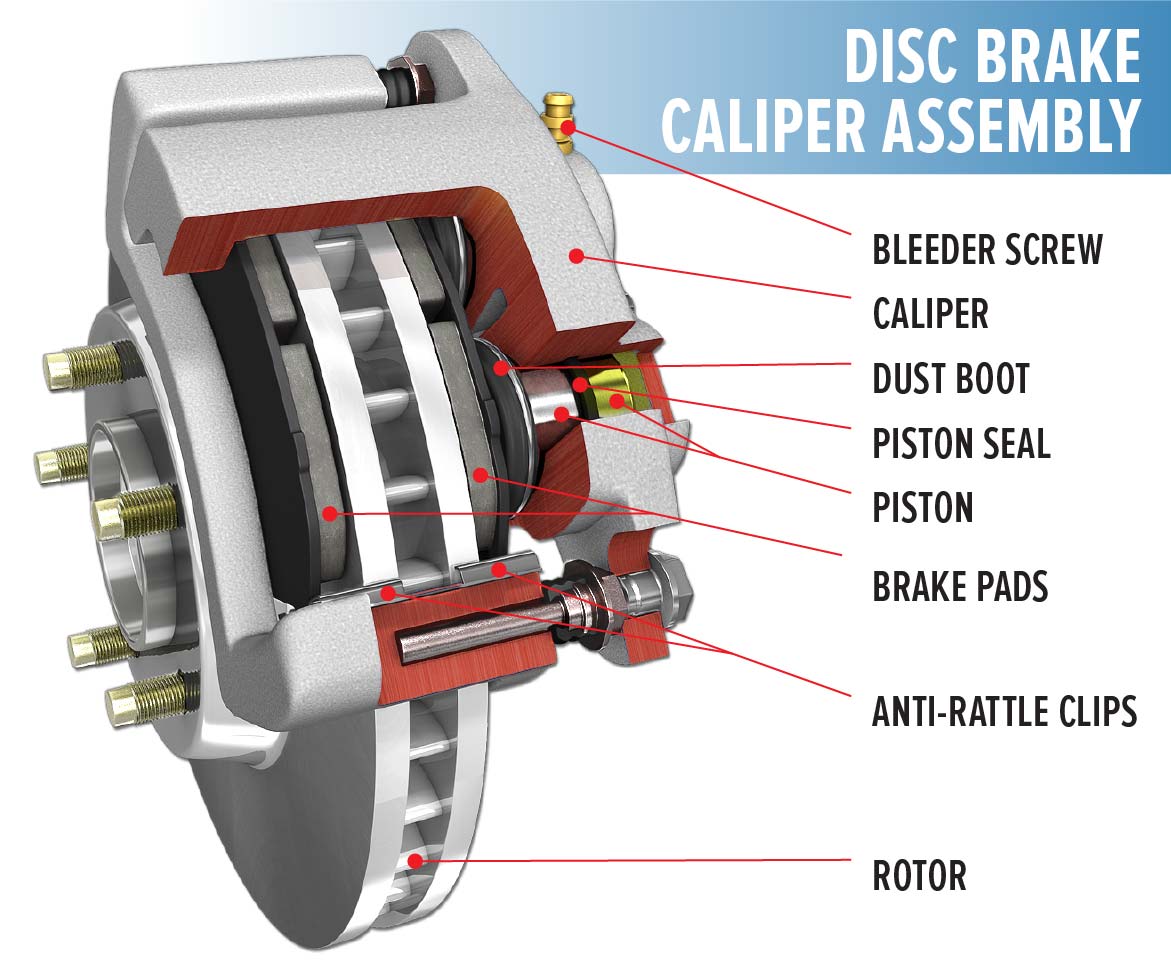
Understanding the purpose of automotive brakes and rotors is essential for grasping their role in ensuring safe vehicle operation. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Deceleration and Stopping: The primary purpose of automotive brakes is to slow down or bring the vehicle to a complete stop. By generating friction against the rotors, the brake system converts the vehicle's kinetic energy into heat energy, allowing controlled deceleration.
2. Enhancing Safety: Brakes play a critical role in ensuring safe driving by allowing the driver to control the vehicle's speed and bring it to a halt when needed, preventing accidents and collisions.
3. Heat Dissipation: Brakes work by creating friction between the brake pads and rotors. The rotors' design allows for efficient heat dissipation, preventing overheating and ensuring consistent braking performance.
4. Reducing Speed: In addition to stopping, brakes enable controlled speed reduction, especially when approaching turns, intersections, or other potentially hazardous situations.
5. Emergency Braking: In emergency scenarios, brakes allow drivers to rapidly reduce speed or stop, helping avoid collisions or minimize their impact.
6. Downhill Control: Brakes help control the vehicle's speed when descending steep slopes, preventing the vehicle from accelerating uncontrollably due to gravity.
7. Regenerative Braking (Hybrids/Electrics): In hybrid and electric vehicles, the braking system can also contribute to energy recovery by converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy to charge the vehicle's battery.
8. Traction Control: By applying brakes selectively to wheels with less traction, modern vehicles with electronic stability control systems enhance traction and stability, especially in slippery conditions.
9. Smooth Deceleration: The interaction between brake pads and rotors enables gradual and smooth deceleration, enhancing driving comfort for both the driver and passengers.
10. Even Brake Pad Wear: The design of rotors contributes to even wear of brake pads, ensuring consistent and predictable braking performance over time.
11. Consistent Braking Performance: High-quality rotors and well-maintained brake pads ensure consistent and reliable braking performance under various conditions.
12. Supporting ABS System: The anti-lock braking system (ABS) relies on the ability of the brake system to modulate pressure on individual wheels. This helps prevent wheel lockup during hard braking, enhancing control and stability.
13. Noise Dampening: The design of brake rotors incorporates features that help dampen noise, reducing brake squeal and other unwanted sounds during braking.
14. Overall Vehicle Control: Effective brakes and rotors are integral to maintaining full control of the vehicle, enabling precise speed adjustments and stops when navigating through traffic, parking, or driving on various road conditions.
By understanding the multifaceted purpose of automotive brakes and rotors, you gain insight into their significance in ensuring safe and controlled vehicle operation.
Understanding common failures of automotive brakes and rotors is crucial for maintaining safe and effective braking performance. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Brake Pad Wear: Over time, brake pads wear down due to friction against the rotors. If not replaced in a timely manner, excessively worn brake pads can compromise braking efficiency and lead to longer stopping distances.
2. Rotor Warping: Continuous heating and cooling during braking can cause rotors to warp or develop uneven thickness. Warped rotors can lead to pulsation or vibrations in the brake pedal and compromised braking effectiveness.
3. Brake Fluid Contamination: Contaminated brake fluid can lead to reduced brake performance and even brake failure. Moisture and air can enter the brake system, affecting hydraulic pressure and responsiveness.
4. Caliper Issues: Brake calipers house the brake pads and play a crucial role in their movement. Sticking or seized calipers can lead to uneven pad wear, reduced braking efficiency, and excessive heat generation.
5. Brake Fade: Brake fade occurs when the brakes lose effectiveness due to overheating. This can happen during prolonged or heavy braking, causing the brake pedal to feel soft and increasing stopping distances.
6. Brake Fluid Leaks: Leaking brake fluid, often caused by damaged brake lines or seals, can result in reduced hydraulic pressure, leading to weakened braking performance or a complete loss of brakes.
7. Uneven Brake Pad Wear: Uneven wear on brake pads can be caused by caliper issues, suspension problems, or misaligned components. Uneven wear can lead to uneven braking force and reduced efficiency.
8. Rotor Scoring: Rotor surfaces can develop grooves or scoring due to prolonged friction with brake pads. Scoring can affect braking performance, increase wear on brake pads, and contribute to noise.
9. Brake Squeal: Brake squeal, caused by vibrations between the brake pads and rotors, can be a result of various factors such as pad material, rotor condition, or improper installation.
10. Rust and Corrosion: In regions with high humidity or exposure to road salt, rotors can develop rust and corrosion. Severe rust can affect braking performance and contribute to uneven pad wear.
11. Brake Fluid Boiling: During intense braking, brake fluid can heat up and boil, leading to a spongy brake pedal feel and reduced braking power.
12. ABS Sensor Issues: Malfunctioning or damaged ABS sensors can affect the operation of the anti-lock braking system, leading to compromised control during hard braking or slippery conditions.
13. Worn Brake Hoses: Cracked or deteriorated brake hoses can result in fluid leaks, leading to reduced hydraulic pressure and compromised brake performance.
14. Excessive Pad Dust: Some brake pads generate more dust than others. Excessive dust accumulation can lead to reduced braking efficiency, increased wear on components, and unsightly wheel appearance.
By understanding these common brake and rotor failures, you can take proactive measures to ensure safe braking, address issues promptly, and maintain the performance and reliability of your vehicle's braking system.
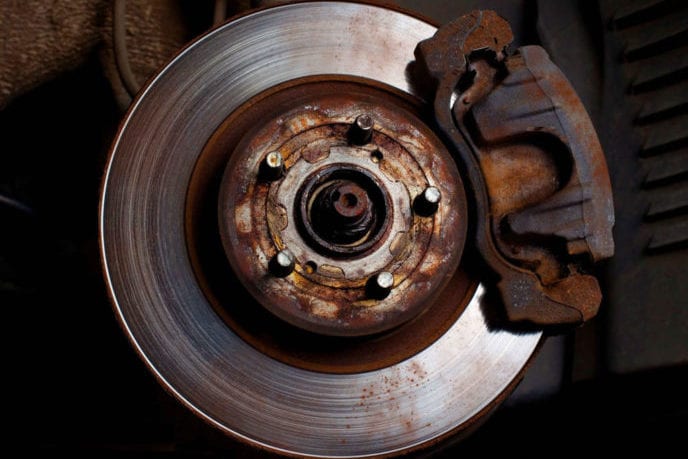
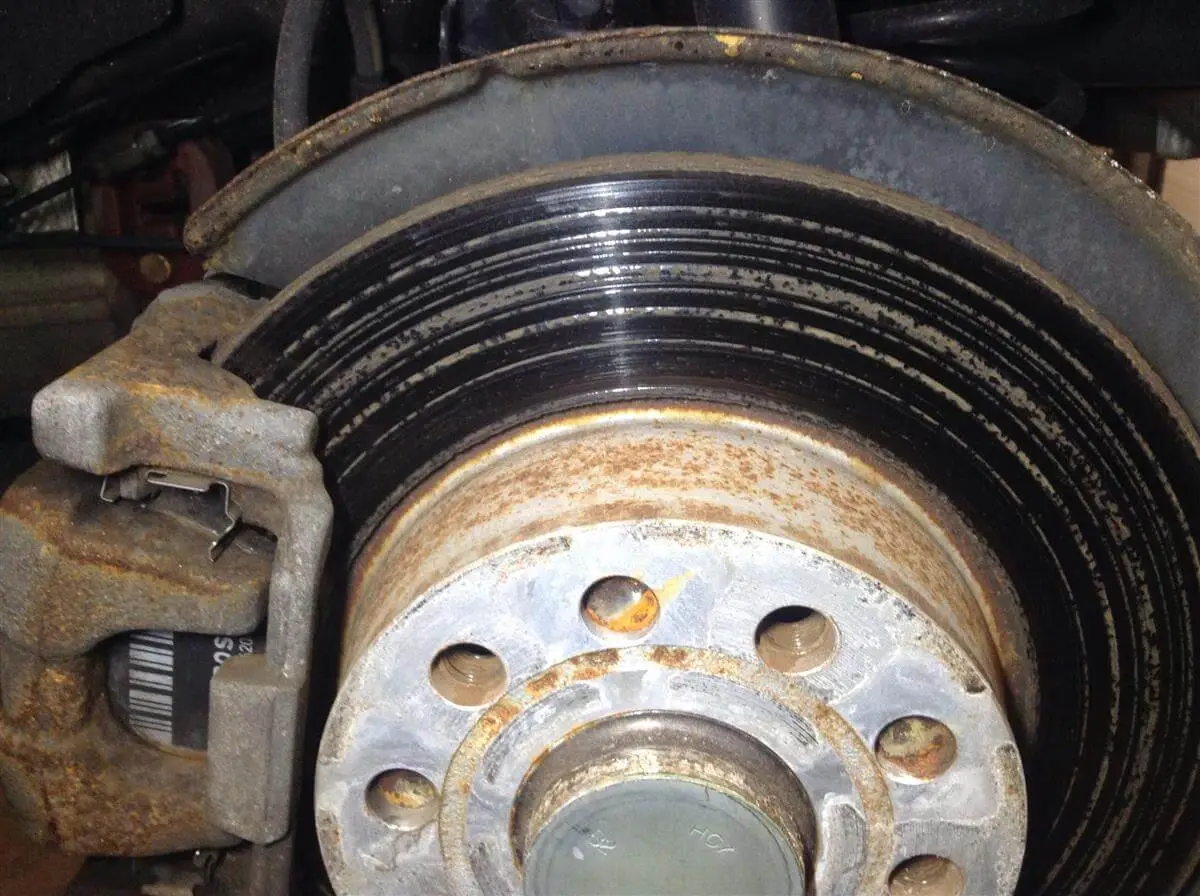
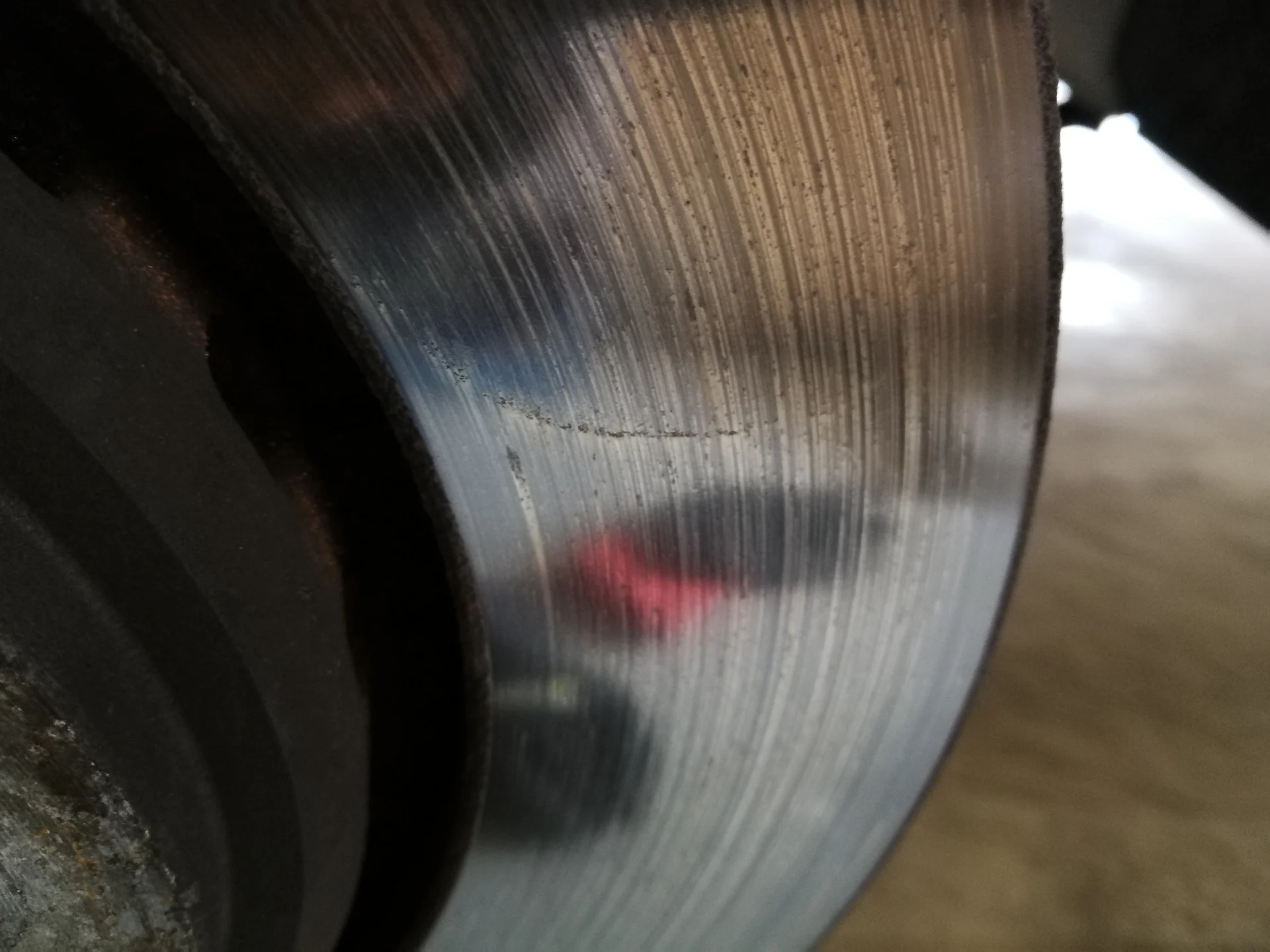
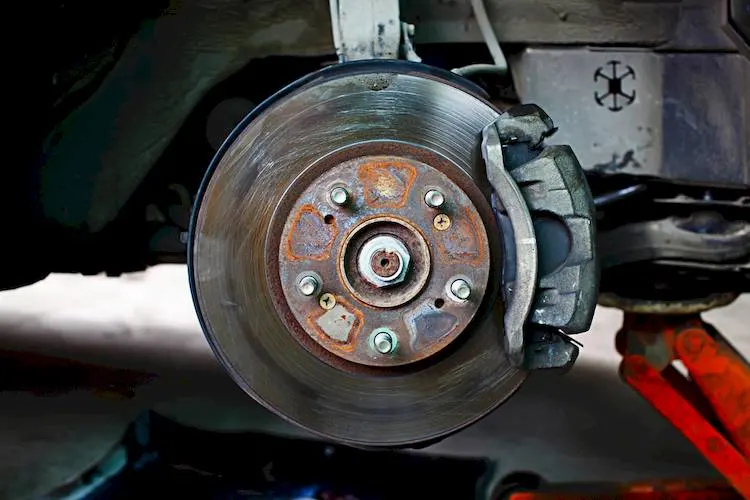
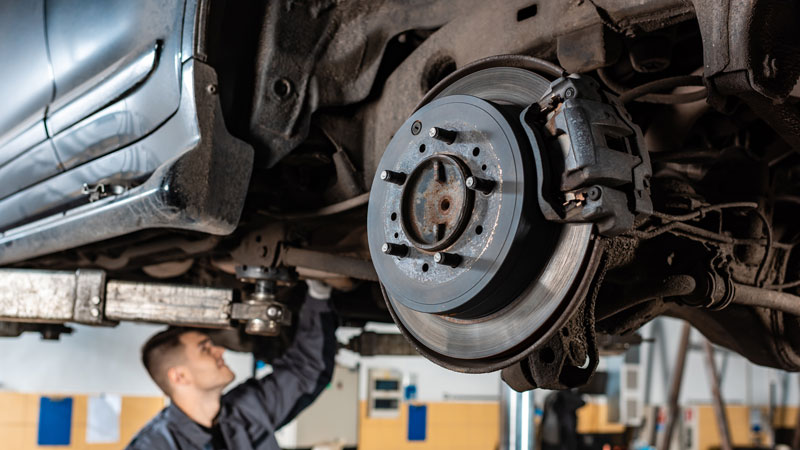
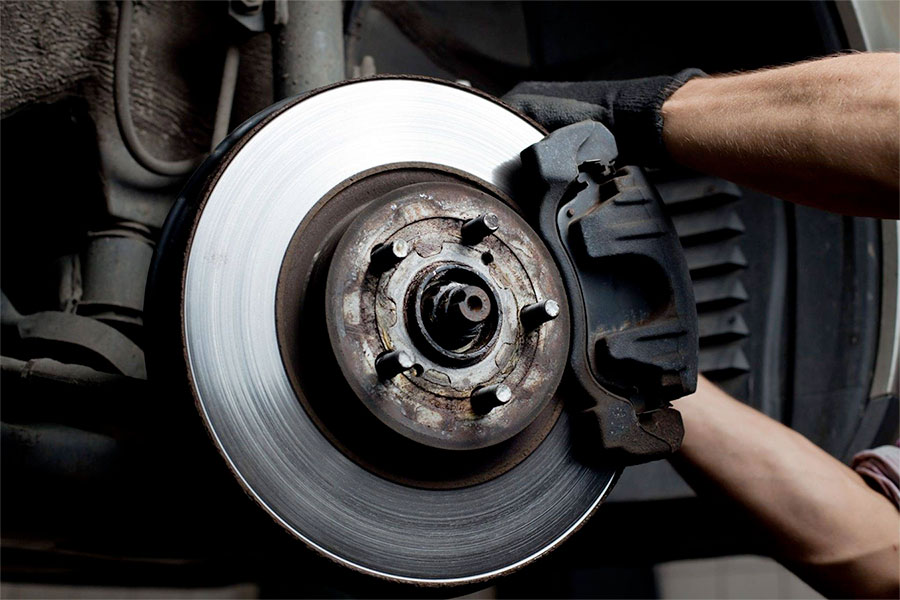
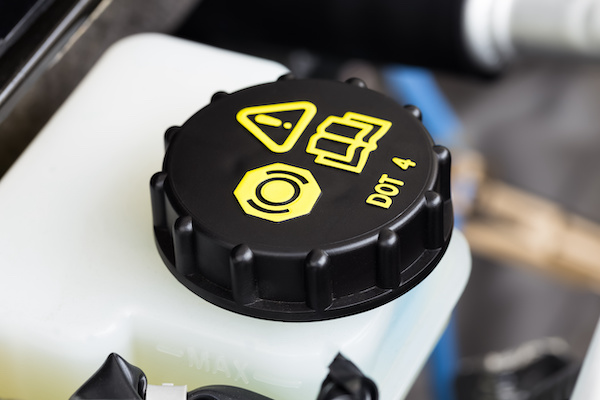
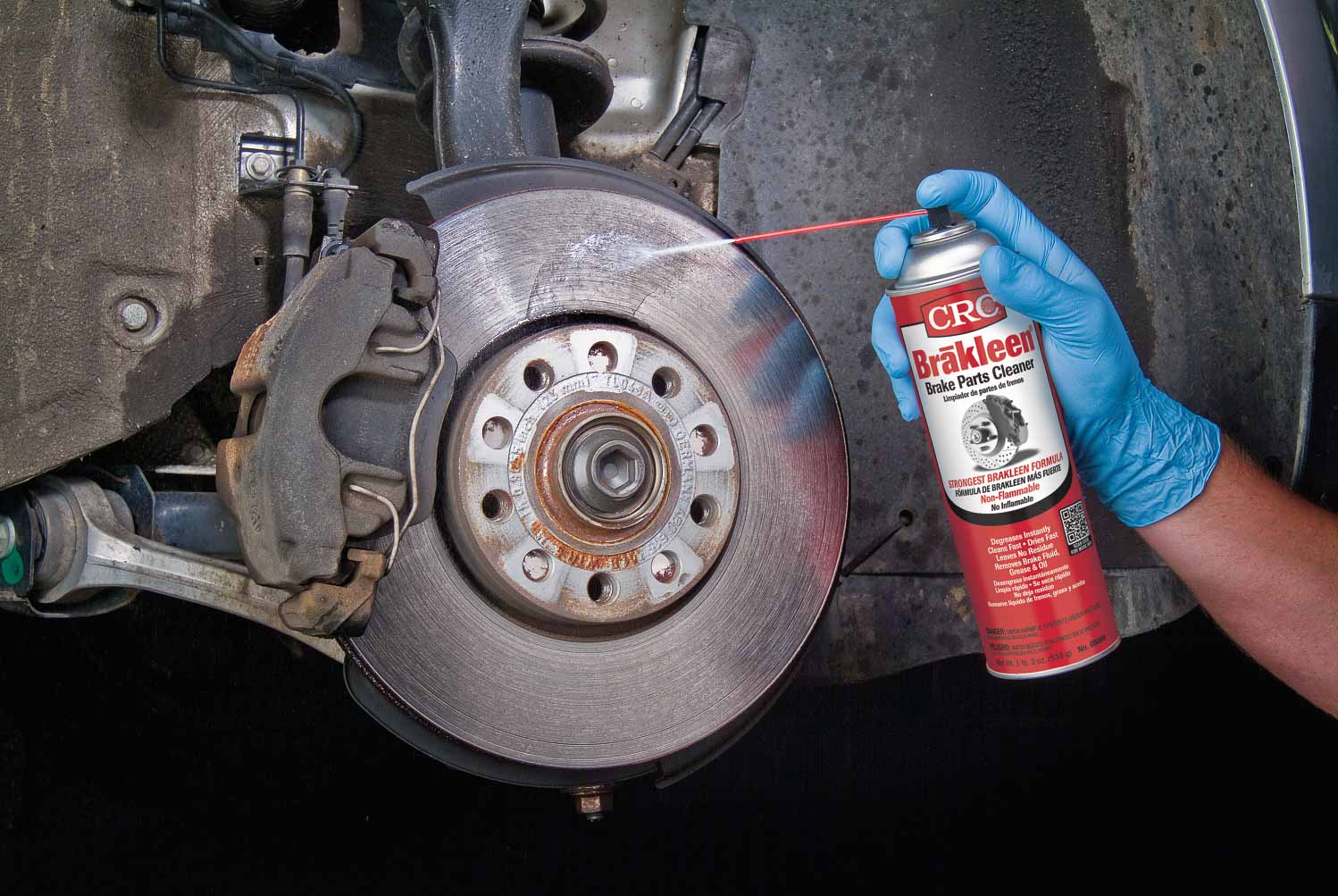










Properly servicing automotive brakes and rotors is essential for maintaining safe and effective braking performance. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Regular Inspection: Include brake and rotor inspection in your routine vehicle maintenance. Regular visual checks can help identify wear, damage, or potential issues.
2. Brake Pad Inspection: Regularly inspect brake pads for thickness and wear indicators. If the pad thickness is approaching the minimum limit or if wear indicators are visible, it's time to replace the pads.
3. Rotor Inspection: Examine rotor surfaces for scoring, grooves, and warping. A visual inspection can help determine if the rotors need resurfacing or replacement.
4. Brake Fluid Check: Check the brake fluid level and condition. If the fluid is discolored or contains contaminants, consider flushing and replacing the brake fluid according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
5. Rotor Resurfacing: If rotors have minor scoring or unevenness, consider resurfacing (also known as machining) to restore smooth surfaces. However, excessive resurfacing can reduce rotor thickness and cooling capacity.
6. Brake Caliper Maintenance: Lubricate caliper slide pins and ensure they move freely. Sticking calipers can cause uneven brake pad wear and reduce braking performance.
7. Pad Replacement: When replacing brake pads, consider replacing all pads on the same axle for even braking force. Follow manufacturer guidelines for choosing appropriate pad materials.
8. Rotor Replacement: If rotors are severely worn, warped, or close to the minimum thickness, replace them. New brake pads may not perform optimally on damaged rotors.
9. Brake System Bleeding: If air enters the brake system, it can affect brake performance. Bleed the brake system to remove air and ensure consistent hydraulic pressure.
10. Brake Hardware Replacement: Replace worn or damaged brake hardware such as clips, springs, and shims to ensure proper pad alignment and prevent noise issues.
11. Caliper Overhaul: If calipers are sticking or leaking, consider overhauling or replacing them. Rebuilt calipers can restore proper function and prevent uneven pad wear.
12. Rotor Cooling: Ensure proper ventilation around the rotors. Clear away debris, rust, or dust to prevent overheating and warping.
13. Brake Fluid Flush: Perform a brake fluid flush at recommended intervals to prevent moisture buildup, maintain hydraulic integrity, and prevent brake fade.
14. Professional Inspection: If you're not experienced in brake maintenance, consult a professional mechanic. They can perform comprehensive inspections and address complex issues.
15. OEM Parts: Consider using original equipment manufacturer (OEM) brake pads and rotors, as they are designed to meet your vehicle's specifications.
By understanding these key points and staying proactive in servicing your automotive brakes and rotors, you can ensure safe and reliable braking performance, contributing to overall vehicle safety.
Let us know how we can help.